Dental Crowns and Bridges
Dental Crowns and Bridges
Crowns are the best option for teeth either when they are attrited or when root canal treatment was performed. Bridges are advised next to implants in cases when there is a single or multiple teeth are missing. There are several varities of crowns present which include metal crown, metal-ceramic crown, LMS crowns, zirconia and solid zirconia
Crowns and Bridges are two different prostheses and are used to restore the natural structure, function, and appearance of teeth that have been damaged or lost.
A dental crown is a tooth-shaped cap placed over a damaged or decayed tooth to restore its strength and shape. It is typically made of porcelain, ceramic, or metal alloys and is designed to fit over the prepared tooth structure.
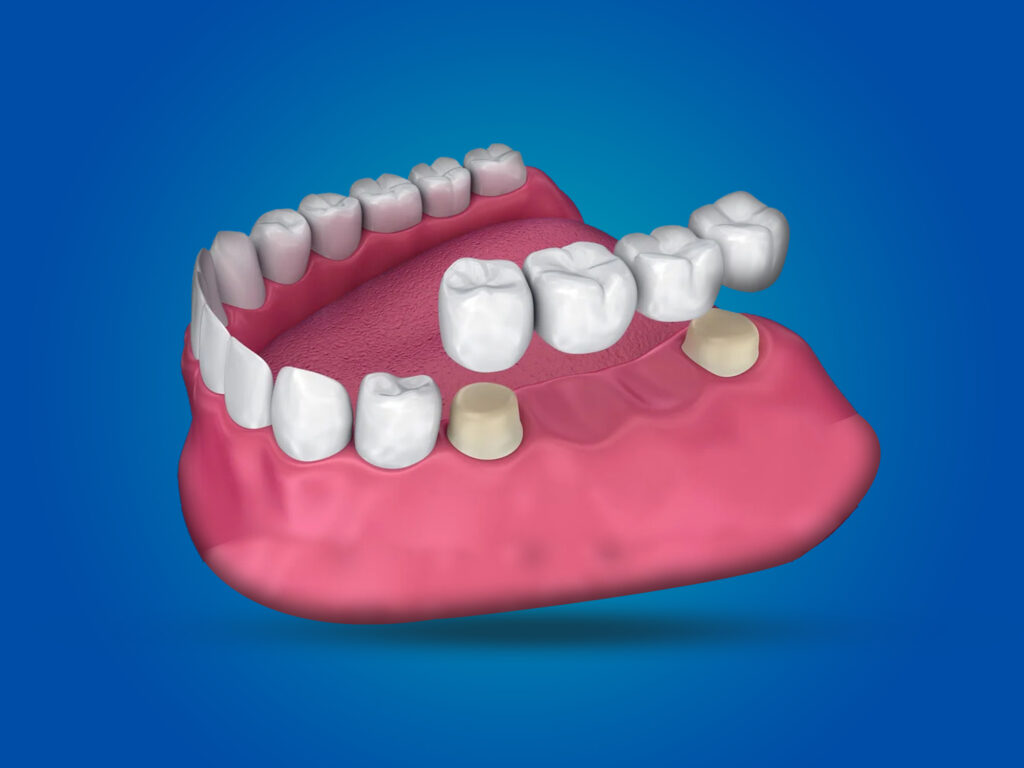
A dental bridge, on the other hand, is a combination of crowns in a unified body that replaces more than one missing tooth. It consists of one or more artificial teeth (pontics) that are anchored in place by two dental crowns, which are placed over the adjacent teeth. The crowns serve as anchors or abutments for the bridge and provide stability and support for the replacement teeth.
Dental Crowns
A dental crown is a cap that covers a damaged or weakened tooth to restore its shape, size, strength, and appearance. Crowns are commonly used when a tooth is:
- Severely decayed
- Cracked or broken
- Worn down
- After a root canal treatment
Types of Crowns:
- Porcelain or Ceramic Crowns: These are the most natural-looking, as they mimic the color and translucency of natural teeth. They’re ideal for front teeth.
- Metal Crowns: Made from alloys like gold or other metals. These are durable and resistant to wear but are more noticeable, so they’re typically used on back teeth.
- Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) Crowns: These combine the strength of metal with the natural appearance of porcelain. They’re a good choice for back teeth but may be less durable than full metal crowns.
Procedure for a Crown:
- Preparation: The tooth is filed down to create space for the crown. If a large portion of the tooth is missing, the dentist may add a filling material to build it up.
- Impressions: A mold of the tooth is taken, and a temporary crown is placed while the permanent one is made.
- Placement: After the permanent crown is ready (usually within a few weeks), it’s placed over the prepared tooth and cemented into place.
Dental Bridges
A dental bridge is used to replace one or more missing teeth. It “bridges” the gap left by a missing tooth by attaching to the adjacent teeth (abutment teeth) or implants. A bridge typically consists of:
- Pontics: The artificial teeth that fill the gap.
- Abutments: The teeth (or implants) on either side of the gap that support the pontics.
Types of Bridges:
- Traditional Bridge: The most common type, where crowns are placed on the adjacent teeth to hold the pontic in place.
- Cantilever Bridge: Used when there is only one adjacent tooth. The pontic is supported by just one abutment.
- Maryland Bridge: This uses a metal or porcelain framework that is bonded to the back of the adjacent teeth, usually without needing crowns.
Procedure for a Bridge:
- Preparation: The adjacent teeth (abutments) are filed down to create space for the crowns that will support the bridge.
- Impressions: A mold of the teeth is taken, and a temporary bridge is placed.
- Placement: After the permanent bridge is fabricated, it is placed and cemented onto the abutments.
Advantages of Crowns and Bridges:
- Aesthetic Improvement: Both crowns and bridges help restore the appearance of damaged or missing teeth, giving you a more natural-looking smile.
- Functionality: Crowns restore the function of a damaged tooth, while bridges restore the ability to chew and speak properly if a tooth is missing.
- Durability: Both are made to last for many years with proper care.
Care and Maintenance:
- Oral Hygiene: Brushing and flossing are essential to maintain the health of the surrounding teeth and gums. Special flossing tools might be recommended to clean around bridges.
- Regular Check-ups: It’s important to visit your dentist regularly to check the integrity of the crown or bridge and address any potential issues.
